Description
Enumeration of micro-organisms: bacteria, fungi and yeasts
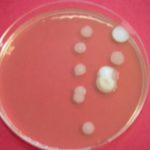
To determine the level of pollution by micro-organisms in a sample, the following procedure is followed:
- Aqueous sample: 0,1 ml of water is spread on Petri dishes.
- Oily sample: oil, fuel, lubricants: 2 ml of the sample is emulsified in 18 ml of a Tween 80 solution. Then 0.1ml of emulsion is spread on Petri dishes. This method is covered by a Qualification Certificate for Special Processes from SAFRAN Laboratories N° AQPS 490.
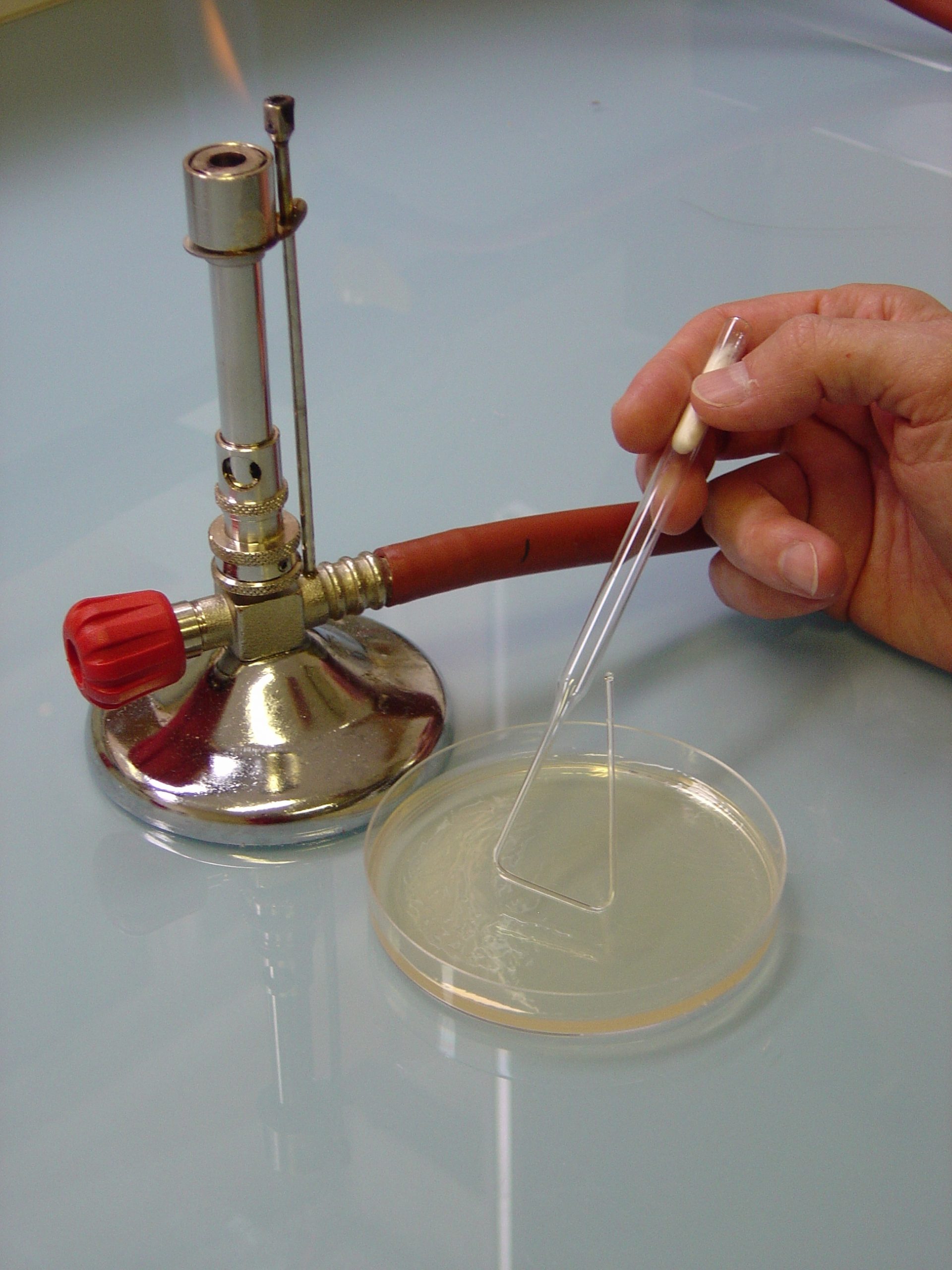
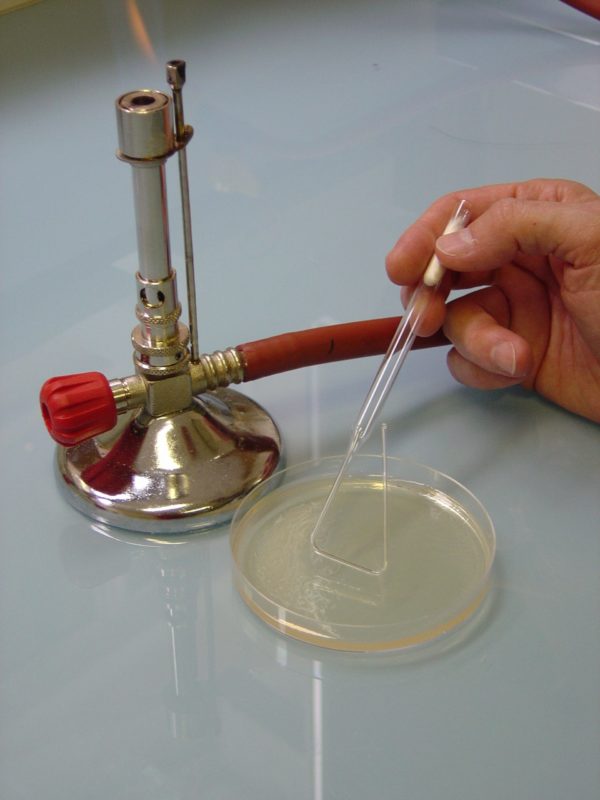
- Surface sampling: using a swab previously dipped in a thinner or a dry swab depending on the surface, take the sample by squaring an area estimated between 20 cm³ and 100 cm³. The swab should be rotated between the thumb and forefinger, making ridges perpendicular to each other. Then return the swab to the tube with the diluent if necessary.
Depending on the micro-organisms being sought, the agar will be adapted. The swab is spread on the agar in a grid pattern, while rotating the swab.

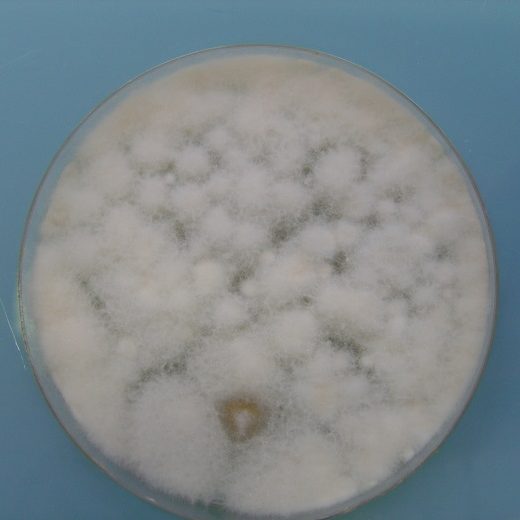
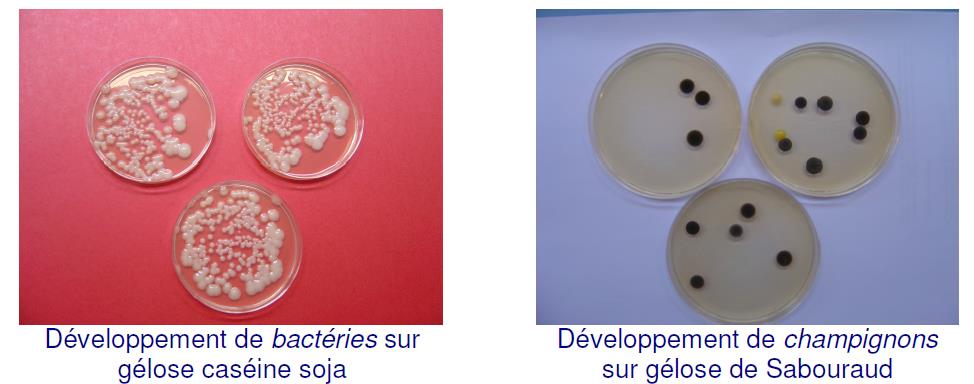
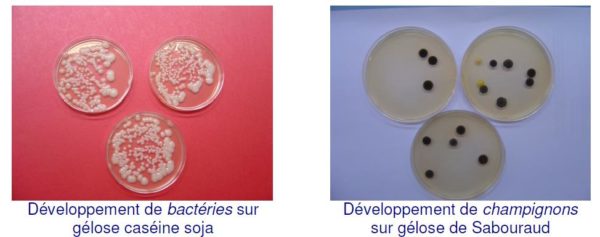
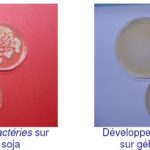
Spreading is done on two types of agar:
- Soy casein agar for aerobic bacteria
- Sabouraud agar for the detection of yeasts and fungi









Notice
There's no notice yet.